Ep #6: Understanding Network Latency: A Beginner's Guide to Why Your Internet Feels Slow
#6: Breaking the complex System Design Components
Have you ever wondered why sometimes your web pages load instantly while other times they seem to take forever? The answer often lies in something called network latency – a fancy term for the delays that happen when data travels across networks. Let's break this down in simple terms so anyone can understand what's really happening behind the scenes.
What is Network Latency?
Think of network latency like the time it takes for a letter to travel from your house to a friend's house. Just as a letter might take longer to reach someone across the country versus someone next door, data traveling across networks experiences similar delays. Network latency is simply the time it takes for information to travel from one point to another in a network.
The Two Main Types of Networks: Internet vs Intranet
When we talk about networks, there are two main types you should know about:
The Internet: The Wild West of Networks
The internet is like a massive highway system connecting millions of computers worldwide. When you visit a website, your data has to travel through multiple networks – some fast, some slow, some reliable, some not so much. It's like taking a road trip where you might encounter traffic jams, construction zones, or detours along the way.
Here's what makes internet communication challenging:
Your data travels long distances (sometimes across continents)
It passes through many different networks and routers
Each network might have different speeds and reliability
Weather, equipment failures, or high traffic can cause delays
Intranet: The Private Highway
An intranet is like a private road system within a company or organization. It's more controlled, typically faster, and more reliable than the internet. Think of it as the difference between driving on busy city streets versus a well-maintained private road with no traffic lights.
Intranet benefits include:
Shorter distances for data to travel
Better maintained and controlled equipment
Less congestion and interference
More predictable performance
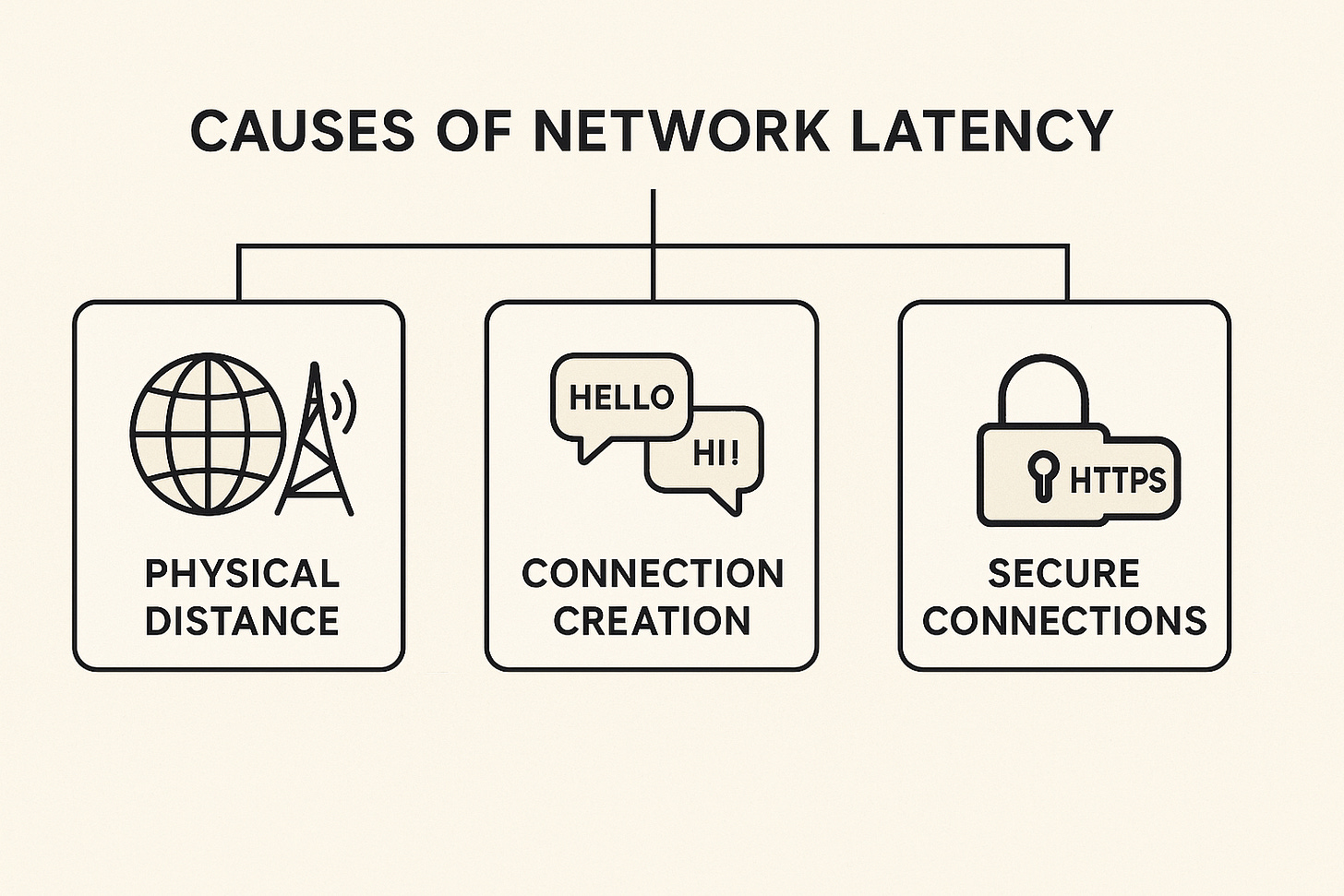
What Causes Network Latency?
Understanding the main culprits behind network delays can help you appreciate why some connections feel sluggish. Let's explore the primary causes:
1. Physical Distance and Data Transmission
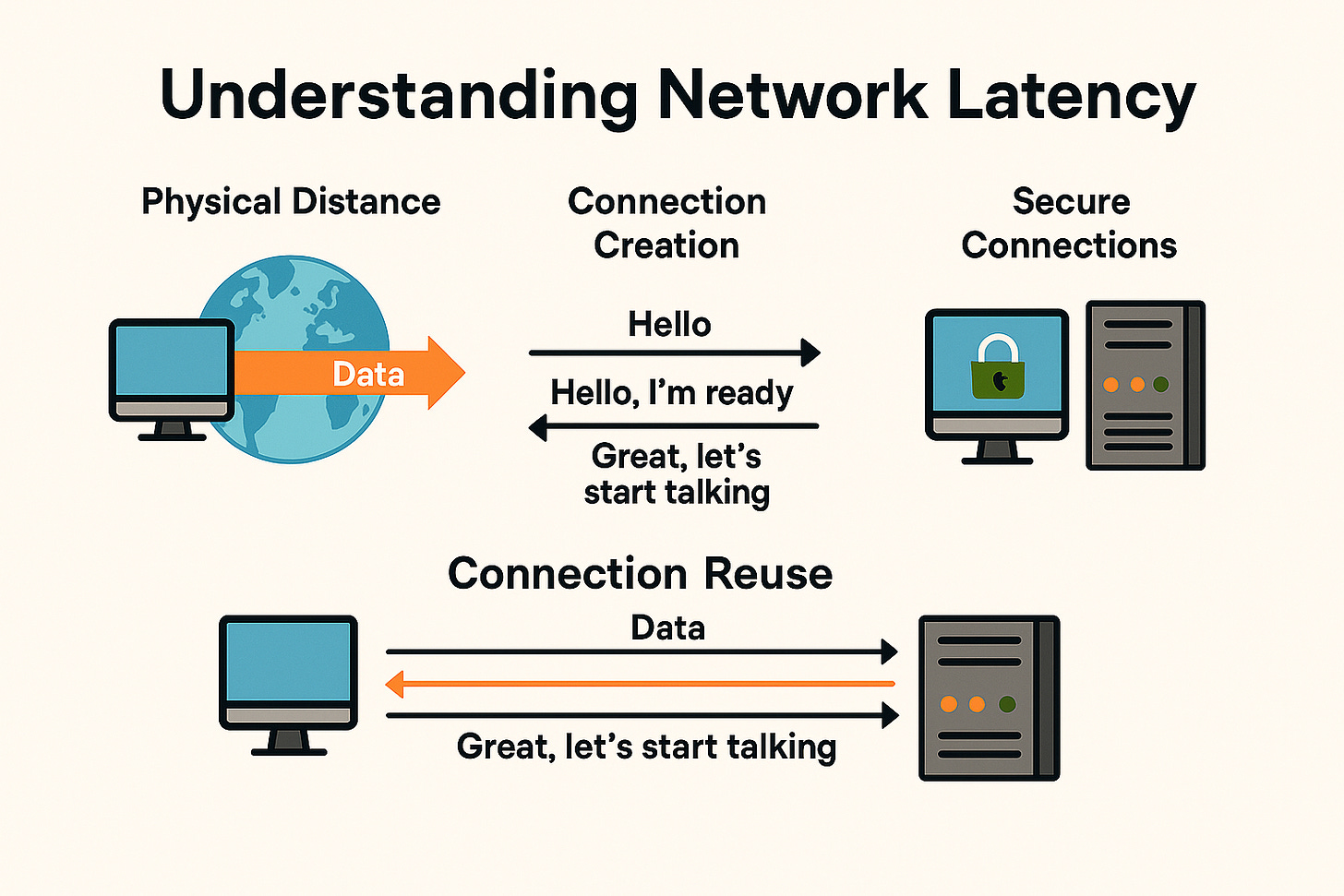
This is the most basic form of latency. Data travels at the speed of light through fiber optic cables, but even light takes time to cover long distances. If you're in New York trying to access a server in Tokyo, your data has to physically travel thousands of miles.
Real-world example: Imagine you're sending a text message to someone on the other side of the world. Even though it feels instant, your message travels through underwater cables, satellite links, and multiple network hubs to reach its destination.
2. Connection Creation: The Handshake Process
Before your computer can talk to a website's server, they need to establish a connection. This is like making a phone call – you dial, wait for the other person to pick up, say hello, and confirm you can hear each other. This process takes time.
Here's how it works with TCP connections:
Your computer sends a "hello" message to the server
The server receives it, processes it, and sends back "hello, I'm ready"
Your computer confirms "great, let's start talking"
Simple example: If each message takes 50 milliseconds to travel, this handshake process alone takes 100 milliseconds before any actual data is exchanged.
Subscribe to get simplified System Design Concepts delivered straight to your inbox:
3. Secure Connections: The Extra Security Steps
When you visit a secure website (those with "https://" and a lock icon), additional steps are required to encrypt your communication. This is like having a secret conversation where you first need to agree on a secret code.
The secure connection process involves:
The regular TCP handshake (1 round trip)
SSL/TLS negotiation to agree on encryption methods (1 round trip)
Key exchange to establish the secret encryption keys (1 round trip)
Breaking it down: If each round trip takes 100 milliseconds, establishing a secure connection requires 300 milliseconds just for the setup, before any actual data transfer begins.
Real-World Impact: Why This Matters
Let's put this in perspective with a practical example:
Imagine you're shopping online and the website needs to load:
The main page
Product images
User reviews
Payment processing page
If each of these requires a separate secure connection, and each connection setup takes 300 milliseconds, you're looking at 1.2 seconds of delay just for connection establishment – before any content actually loads!
The Bigger Picture
Network latency affects everything we do online:
Video calls: Delays can cause that awkward "you go first, no you go first" dance
Online gaming: High latency can mean the difference between winning and losing
File downloads: What should take minutes might take much longer
Web browsing: Pages feel sluggish and unresponsive
What Can Be Done?
While we can't change the speed of light or eliminate distance, there are strategies to minimize latency:
Connection reuse: Instead of creating new connections for each request, reuse existing ones
Content delivery networks (CDNs): Place servers closer to users
HTTP/2 and HTTP/3: Newer protocols that handle multiple requests more efficiently
Compression: Reduce the amount of data that needs to travel
Looking Ahead
Understanding network latency is the first step toward building faster, more efficient web applications. In our next article, we'll dive deeper into specific techniques and strategies that developers use to minimize these delays and create snappier user experiences.
Key Takeaways:
Network latency is the delay in data transmission across networks
Internet connections are slower and less reliable than intranet connections
Connection establishment creates significant overhead, especially for secure connections
Understanding these fundamentals helps explain why some online experiences feel slow
There are practical solutions to minimize latency impact
Remember, every millisecond counts in creating a smooth user experience. By understanding these concepts, you're better equipped to make informed decisions about web performance and user experience optimization.